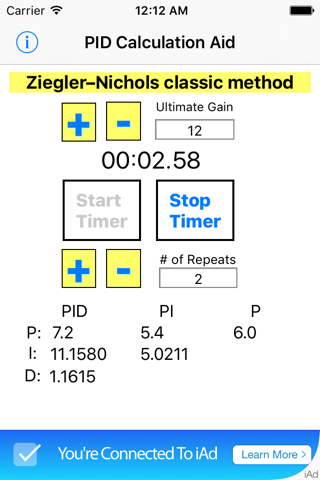
This program is based on Ziegler-Nichols classic method for approximating PID control values.
Operation:
1) Clicking the Ultimate Gain "+" or "-" will increase or decrease the Ultimate Gain value by 0.1 or you may tap the value and enter a value manually.
2) Clicking the # of Repeats "+" or "-" will increase or decrease the # of Repeats value by 1 or you may tap the value and enter a value manually.
3) The Start Timer and Stop Timer controls are used to find the oscillation period.
This can be done using the buttons on the screen or by clicking the volume button(s). Click the time display to manually enter the time.
4) Clicking on the Time will offer the user a new window to adjust manually the time used in the calculation.
5) The resulting PID values should be used as a good starting point as most systems still require a small amount of manual tuning or a different method of calculation.
Notes:
Use this software by first setting the intended targets control Integral and Derivative values to 0 on the process to be tuned. Next, starting from 0, raise the Proportional value in small increments until the system oscillates at a steady rate around the set-point. Record this value as the Ultimate Gain and enter it into this softwares Ultimate Gain text-box. Next enter the amount of repeats to be used in the calculation into the # of Repeats text-box. Wait to start the timer until the next oscillation cycle begins and stop the timer when the systems number of cycles matches the specified repeat amount. choose the P , PI, or PID column and test the result by changing the intended targets proportional to the P, I, and D values chosen . Next, slowly increase the Integral value from 0 until equal to the I value chosen or a desired result is achieved. Slowly increase the derivative from 0 until equal to the D value chosen or a desired result is achieved.
More Information on PID Tuning may be found online @ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PID_controller
